SEO Glossary
Stumped by all the jargon in organic search?
We know there’s a lot.
That’s why we’ve put together an SEO glossary.
Start building a basic understanding of what these terms mean.
Algorithm: A type of software Google has that it uses when it ranks pages for different keywords.
There are multiple different ranking signals Google checks for. These algorithm changes can happen throughout the year. Find out more about Google core updates.
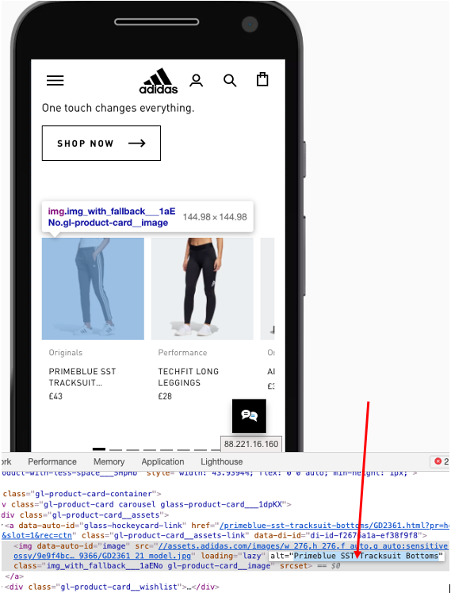
Alt text: the words that act as the label to describe an image.
Best practice is to have an alt text that describes what’s in the image. Then, optimise it by including your target keyword for that page. We’ve grabbed an example so you can see what it looks like in the code of your page.
Anchor text: the words that are clickable on a piece of copy that has a link, either internal or external.
This anchor text should include words that tell Google and your user what the linked page is about, and ideally include the keyword for that linked page.
Backlink: When one page from an external domain (a domain that’s not yours) links to your page/domain.
Blog: Content that’s outside of the realm of the home page, product pages or category pages.
They are informative, helpful pages that your audience should enjoy reading and gain relevant knowledge from.
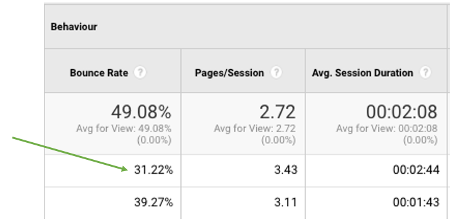
Bounce rate: The rate at which your users tend to exit a given page, and leave the website completely.
This is calculated by how many sessions each page gets and how many of those sessions then end by that session user exiting the website. You’d want to aim for a less than 55% bounce rate, roughly. Otherwise, depending on the page, this should cause alarm bells.
Cannibalisation: When different pages are ranking for the same keyword.
This can be unintentional but it can damage your SEO performance because it confuses Google.
If you have similar forms of content across your website that ranks for the same keyword, Google won’t know which one you really want it to rank as the most effective and important listing for that keyword.
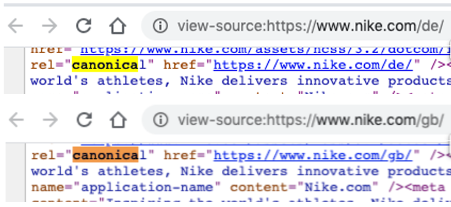
Canonical: When you have more than one URL with seemingly the same content on, you can add a canonical tag to both of the pages that tells Google which one is the canonical.
The canonicalised one is the page you want to rank. You might add a canonical to location specific URLs, so people in different countries can access the right translated versions. It looks like this:
CMS: Content management system, like WordPress or Joomla.
This is where all of the changes are made to a website.
Click-through rate: The number of people who search for a keyword and see your listing, compared to the number of people who see it and actually open the link to your website.
It’s also known as CTR.
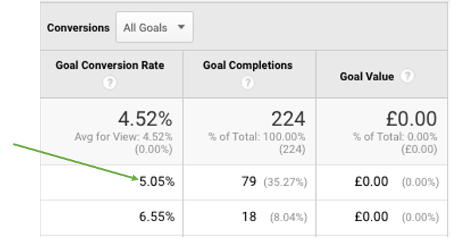
Conversion: When a user takes the action at the bottom of the funnel, such as making a purchase or sending an enquiry.
You can see this per page and per goal in Google Analytics, where a goal might be a form fill submission, or reaching a ‘thank you’ page after buying a product. It looks like this:
Crawl: When Google finds and accesses your site, it needs to ‘read’ everything on it.
That means the sitemap, the pages, all links and so on. This process is called crawling, and it does this before it indexes your site, so it can rank your pages.
Crawl budget: Google has a set crawl budget. This is the number of pages that it can crawl to be indexed each time it does so.
This is why it’s important to use your robots.txt file effectively, so to not waste Google’s crawl budget. You might set irrelevant or unimportant pages to be noindexed, so that only the pages you want to show up the listings get indexed.
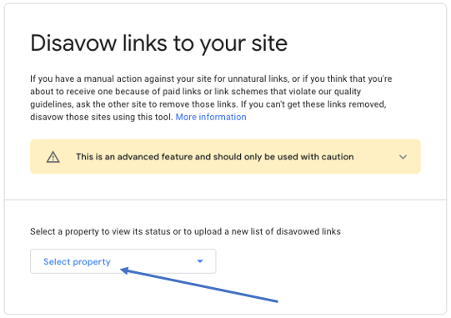
Disavow: A ‘disavow’ is processed when you don’t want a link to be associated with your domain, if it’s of poor quality or from a low domain authority for example.
You can send a request via Google Search Console for Google to remove the association between the link you want to be disavowed. You do this by going to Google’s disavow tool, selecting your Property (you’ll need to set this up in Google Search Console), and uploading a list of domains you want to disavow.
Domain authority: The strength of a site which has been decided over time.
Big time SEO players Moz created a ‘domain authority score’ that’s set between 0 and 100, and Google does take this into account before it ranks a page. Find out more about domain authority in SEO.
Duplicate content: When there are instances of the exact same copy on one or more different URLs on a site.
Best practice is to aim for unique content. Read more information on duplicate content in SEO.
Featured Snippet: A featured snippet is a short type of text that can appear at the top of the Google listings.
It gives the reader a quick answer with information they’re directly looking for, and is known to have an exceptionally higher CTR, of 23% (according to 2020 data). There are different ways information can be displayed, like a step by step set of instructions, a bulleted listicle or a short paragraph.
But here is an example of a keyword with a search volume of 880 that shows a featured snippet result. So, 880 (SV) x 23% (CTR) = 205 click throughs.
H tags: Headings that are designed to break up and structure content. They’re also one of Google’s high value parts of the page it checks when it indexes, so it’s best practice to optimise these.
HTTP: A URL that is not secure
HTTPS: A URL that is secure.
This protocol is best practice to have, to show Google your website is secure and safe for users to land on.
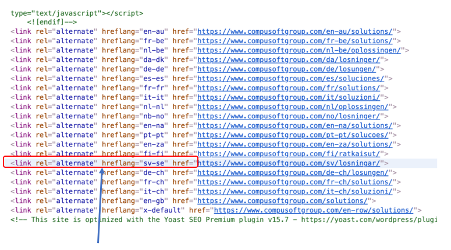
Hreflang: A code that is used to tell Google it’s the same content, but it’s written in a way that’s targeted for different languages or locations. It goes in the sitemap, can be a HTML tag or in the HTTP header, and it looks like this:
Indexing: When Google has accessed and read a page, and then stores it, so to speak, so that it can rank it.
Infographic: A visual piece of content in the form of imagery rather than copy only
Internal link: A hyperlink from one page on your domain to another page on that same domain. Find out more about internal linking in SEO.
Keyword: A word or phrase that has at least one word in that a user has searched into Google.
Keyword density: This means how many times the keyword appears on that page.
Keyword difficulty: How hard it is estimated to rank for that given keyword, based on competition and search volume.
Keyword research: The process of looking for and finding a set of keywords you want to optimise any given page for. Find out what keyword research for SEO is.
Keyword stuffing: When a keyword is mentioned too many times on the page, making the copy potentially read unnaturally. This can not only put people off reading your content, and also cause a drop in rankings if Google notices this.
Link building: The process of growing your link profile, which is the number and quality of your external links.
Gaining natural backlinks can take time and resource and isn’t always successful. It is best practice to create super high quality content that companies will want to link to. You can check out our guide on writing for SEO, or read the top 10 link building myths in SEO.
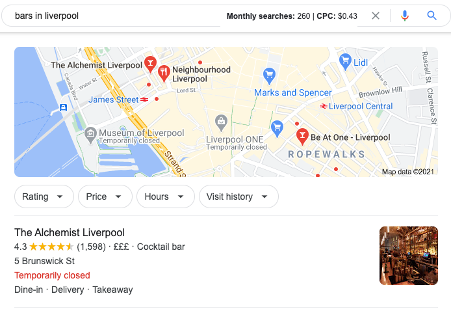
Local queries: Search terms that have a geographical inclusion.
For example the keyword might be “shoe shops near me” or “bars in Birmingham”, but here is an example result.
Long tail keyword: A keyword that has 3 or more words as part of the search term.
These can often be prefixed with: what, why, how, when, who.
Meta data: The collective phrase that refers to the meta title and description together.
See the example below of where the meta title and description can be found. The red arrow points to the meta title, and the green arrow points to the meta description.
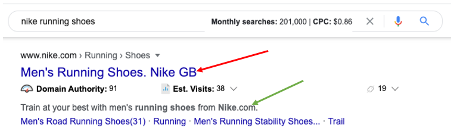
Meta description: The copy that sits underneath the meta title
Meta title: This is the blue title text that’s the first part of the listing
Mobile first: This refers to when Google started taking notice of how websites perform on mobile, as well as desktop (and tablet), as of 2018.
Nofollow: The link juice, or strength, isn’t being passed from the one link to the other.
However, if you receive a nofollow link, you will still receive referral traffic from any website users who click that link, which Google will recognise.
Orphan page: A page on a domain that has no internal links anywhere else on that domain.
Best practice is to avoid these at all times if that page is to rank, otherwise Google won’t understand how that page connects to other pages on the website.
Pagination: when a website owner uses a tag like rel=”prev” and rel=”next”, for example on an ecommerce page of product listings. It indicates to Google how these pages relate to each other, and Google acknowledges that the user should really be sent to the first page in that sequence.
Redirect: when a page gets moved to another location, it gets ‘redirected’ so that the user can find that page automatically, and doesn’t land on a broken page. There are permanent redirects and temporary redirects.
Robots.txt: a crawl directive, or a way of telling Google which pages you do and don’t want to be crawled indexed. Find out more about how robots.txt work in SEO.
Search volume: The amount of times that keyword has been entered into Google on average that month. Use the below example to see where to find search volume if you use Google Keyword Planner.

SEO: SEO stands for search engine optimisation and refers to the entire concept of making on page, off page and off site changes to boost your organic visibility, causing an increase in website traffic and conversions. Find about what SEO is.
Sitemap: A list of every single URL that sits on your domain, usually can be found by accessing the following: www.yourdomainname/sitemap.xml
Site speed: How fast your site or a given page on your domain loads and functions for the user. This can affect your ability to rank. Find out why site speed matters in SEO and how to improve.
Structured data: A way of labelling your content so that Google understands what the page is for. For example, you can label it as a ‘recipe’ or ‘product’. You can do this using Schema.
Thin content: When a page has such a low amount of copy on, it can be classed as ‘thin content’. Google can then struggle to know where to rank this page, if it’s set to be indexed.
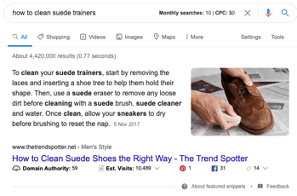
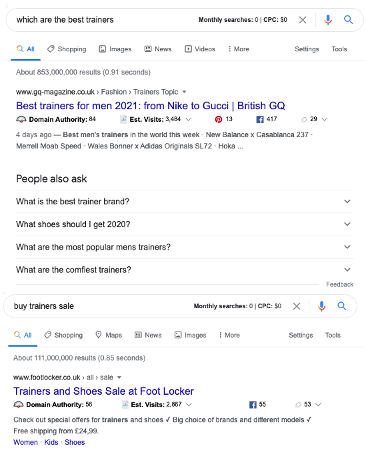
Transactional queries: A search term that suggests the user is much further down the marketing funnel.
They are ready to purchase from you, rather than only looking for more topic information. For example, “buy trainers sale” is transactional which is why it shows more ecommerce results focused on online shopping. But “which are the best trainers” is likely to be an information search, which is why it shows a helpful guide and a People Also Ask feature. See below the difference in the SERPs.
Bonus jargon! What do these codes mean?
404: An error page, a broken page
301: This page has been permanently redirected.
302: This page has been temporarily moved.
5xx: Error code that is related to a server problem.
2xx: The page was accessed and loaded successfully.
We hope our SEO glossary helps clear things up, but if you’re still a little confused or have any questions, you can get in touch.
Or head to our digital marketing blog, where we have an abundance of information, all things SEO.
We’re talking about the latest updates on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and LinkedIn too.